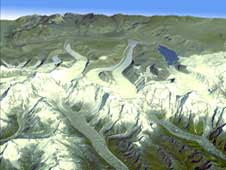
So many disparate elements, both natural and man-made, converge in the Himalayas," said William Lau, a climatologist from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "There’s no other place in the world that could produce such a powerful atmospheric heat pump," referring to a new hypothesis he’s put forward to explain the rapid retreat of Himalayan glaciers in recent decades.
The Himalayas, home to the tallest mountains on Earth, include more than 110 peaks and stretch 2,500 kilometers (1,550 miles). Bounded to the north by the Tibetan Plateau, to the west by deserts, and to the south by a bowl-like basin teeming with people, the mountains hold 10,000 glaciers.
These massive rivers of ice spill off mountain sides and grind down through creviced valleys. In the spring, when the monsoon carries moist air from the Indian Ocean, the glaciers begin to thaw, replenishing lakes, streams, and some of Asia's mightiest rivers, on which more than a billion people depend.
South of the Himalayas -- which forms the east-west edge of the table-like Tibetan Plateau -- the mountains give way to the Indo-Gangetic plain, one of the most fertile and densely populated areas on Earth. The plain has become a megalopolis of cities including Delhi, Dhaka, Kanpur, and Karachi, as well as a hotspot for air pollution, with a steady supply of industrial soot mixing with ash and other particles in the air.
No comments:
Post a Comment